Liaison mechanism
Liaison Mechanism
This instrument combines a tariff on imports with a production subsidy. Note: different from an export subsidy, here the Home country is not an exporter. The main idea behind it is to boost local production, and this instrument contributes to this end by two means:
- With the tariff, the price at home increase, increasing local production,
- With the production subsidy, local production is encouraged even more.
In general, liaison mechanisms are established such that the entire revenue coming from the tariff is used to pay production subsidies.
Effects of a liaison mechanism
To simplify things, we focus on a small, open economy that imports a good.
The first step consists on adding a tariff on imports, we assume it is an ad-valorem tariff, though.
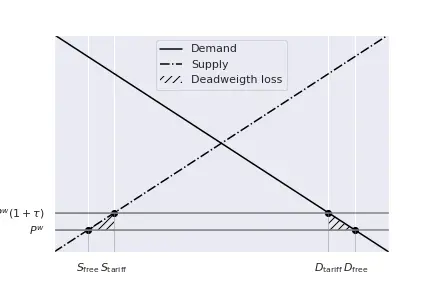
For a small country, we already know that this represents a deadweight loss, and that the price payed by the consumers equals $p^w(1+\tau)$.
At this stage, the tariff levied by the government is equal to $p^w \tau (D_\text{tariff} - S_\text{tariff}).$ Next, these proceedings are used to finance a production subsidy at the rate $s$, which further increases the priced received by the producers to $(p^w(1+\tau)(1+s).$ At the same time, local production increases, which implies that less imports are required, thus reducing the amount of income the government levies. Is is possible to mathematically balance the two such that the entire amount coming from the tariff is used to finance the production subsidy. Note, however, that the introduction of the production subsidy does not change the quantity nor the price faced by the consumers. Thus, the situation is as follows:
- Since local production increases, imports decrease to $D_\text{tariff} - S_\text{subs}.$
- Consequently, tariff revenue also decreases to $p^w \tau (D_\text{tariff} - S_\text{subs}).$
- The total amount payed as subsidy is $p^w(1+\tau)s S_\text{subs}.$
- $p^w \tau D_\text{tariff} - S_\text{subs} = p^w(1+\tau)s S_\text{subs}.$
Overall, we observe that production moved from $S_\text{free}$ to $S_\text{subs}$ and producers earn $p^w(1+\tau)(1+s).$
Demand shrinks, as with all tariffs: $D_\text{free}$ to $D_\text{tariff}.$
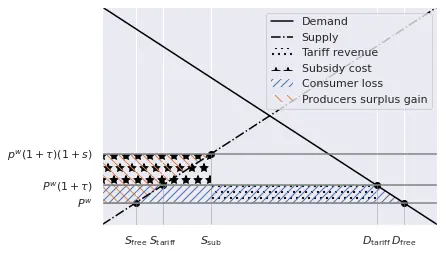
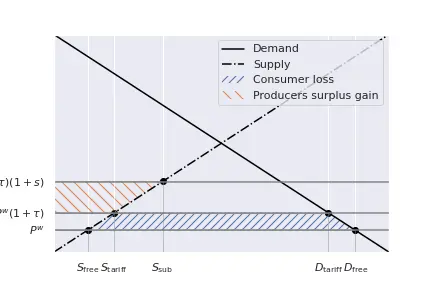
The consumers loss the blue-shaded area, while producers gain the orange surface.
The effect for the government is neutral: as we said, tariff income (dotted area) is equal to the subsidy (star area).
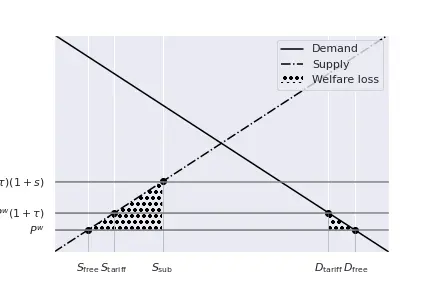
So, we shall compare the following areas: